Importance of Quality Sleeping
World Sleep Day, an annual initiative organized by the World Sleep Society, serves as a vital reminder of the significance of quality sleep and the management of sleep-related issues.
Typically observed on the Friday preceding the spring equinox, this day sheds light on the profound impact insufficient rest can have on overall health.
Sufficient naps are crucial for numerous bodily functions, including immune system strength, metabolic balance, hormone regulation, and heart health. It also plays a pivotal role in cognitive and emotional well-being, fostering memory, learning, problem-solving, and emotional stability.
Sleep Deprivation: The Silent Monster
On the other hand, poor sleep habits have been associated with a higher risk of chronic ailments like obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and stroke. Moreover, persistent deprivation can worsen mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Occurring when an individual fails to obtain adequate sleep, deprivation, whether for a short-term spanning a few nights or persisting as a chronic concern lasting weeks or even months.
Understanding the nuances of sleep deprivation and its potential implications emphasizes the importance of prioritizing restorative resting habits and seeking professional guidance when necessary.
The optimum daily resting hours by age is :
- Newborns (up to 3 months): 14 – 17 hours.
- Infants (4 – 12 months): 12 – 16 hours
- Children (1 – 5 years): 10 – 14 hours.
- School-aged children (6 – 12 years old): 9 – 12 hours.
- Teenagers (13 – 18 years old): 8 – 10 hours.
- Adults (18 + years): 7 – 9 hours.
Deprivation is not linearly defined as inadequately. Rather, it can take several forms and is also manifested when individuals cannot find quality sleep and feel lethargic after waking up.
Effects of Sleep Deprivation
It can have far-reaching consequences on various body systems and processes, impacting overall health and well-being:
- Heart and Circulation: Chronic sleep deprivation increases the risk of hypertension and high cholesterol (hyperlipidemia).
- Metabolic Systems: Individuals become prone to developing Type 2 diabetes due to disrupted metabolic processes.
- Immune System: Lack of rest affects body’s ability to fight off infections effectively.
- Nervous System: Insufficient resting often leads to heightened pain sensitivity, resulting in increased perception and intensity of pain.

- Brain Function: It impacts learning, memory, and cognitive processes. It may even cause neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
- Mental Health: Deprivation can exacerbate mental health conditions. Heightened stress, difficulty to manage emotions, depression and anxiety are observed.
Are you sleeping well?
Asses the 10 signs and symptoms and answer the question!
- Fatigue and Daytime Sleepiness: Persistent tiredness and drowsiness during the day.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Impaired cognitive function resulting in challenges with focus, memory retention, and alertness.
- Mood Changes: Increased irritability, mood swings, and heightened sensitivity to stressors.
- Impaired Motor Skills: Reduced coordination, slower reaction times, and clumsiness, posing a risk of accidents.
- Increased Appetite and Weight Gain: Changes in appetite, cravings for high-calorie foods, and subsequent weight gain.
- Headaches: Tension headaches or migraines may occur more frequently and persistently.
Better your Resting Routine!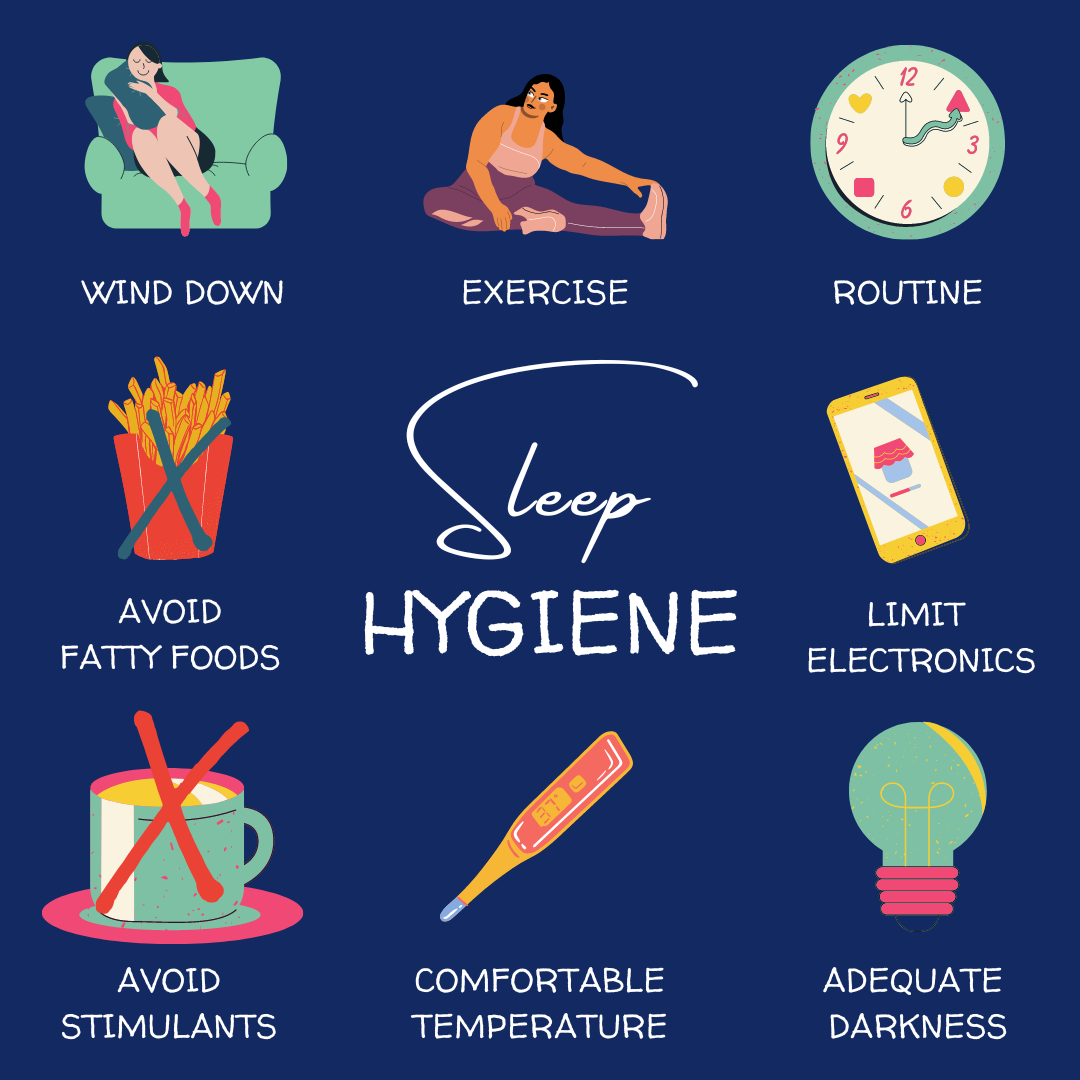
- Establishing Consistency: Maintain a regular nap schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day to regulate your body’s internal clock.
- Creating a Relaxing Routine: Develop a soothing bedtime routine involving activities like reading or meditation to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down.
- Limiting Stimulants: Avoid consuming caffeine and using electronics before bedtime to prevent disturbances.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing or mindfulness meditation to relax before dozing off.
- Optimizing Environment: Ensure a comfortable sleep environment with cozy bedding, and minimal noise and light for better nap quality.
- Mindful Eating: Avoid heavy meals and alcohol close to bedtime, opting for a light snack if hungry.
- Stay Active: Engage in physical activity, even a simple walk, to improve nap quality.
- Use Medications Wisely: Avoid relying on over-the-counter sleep aids and consult a healthcare provider for proper prescription and usage guidance.













Comments 1